| Lessiniabatis Temporal range: | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Chondrichthyes |
| Subclass: | Elasmobranchii |
| Superorder: | Batoidea |
| Order: | Myliobatiformes |
| Superfamily: | Dasyatoidea |
| Genus: | †Lessiniabatis Marramà et al 2019 |
| Species: | †L. aenigmatica |
| Binomial name | |
| †Lessiniabatis aenigmatica Marramà, Carnevale, Giusberti, Naylor & Kriwet, 2019 | |
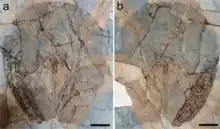
Lessiniabatis is an extinct genus of highly unusual stingray from the Early Eocene of Italy. It contains a single species, L. aenigmatica. It is known from three specimens, one nearly complete, from the famous Monte Bolca lagerstätte.[1][2]
Taxonomy
The specimen was initially assigned as the holotype of Arechia crassicaudata, another fossil stingray from the same formation, which was found to be made in error as Lessiniabatis does not share any of the diagnostic traits of A. crassicaudata. It was later described as its own genus and species in 2019. Phylogenetic analyses recover it as a derived member of the Dasyatoidea, and the sister group to the Dasyatidae and Potamotrygonidae.[1]
The genus name references Lessinia, the Italian geographical area where Monte Bolca is located, while the species name references its strange appearance.[1]
Description
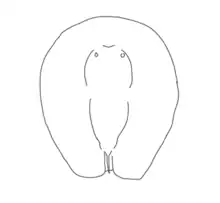
Lessiniabatis is notable for its bizarre body plan, which has no analog in any other stingray, fossil or modern. It had a disc-shaped body akin to modern benthic stingrays, but its tail was highly reduced to become very short and slender, with an apparent loss of the tail sting. The pectoral radials were fused with one another, potentially as an adaptation to strengthen the undulations of its body as it swam.[1][3][4]
Ecology
The unusual adaptations of Lessiniabatis may reflect an evolutionary radiation in new body plans by cartilaginous fish following either the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event or the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum. The Monte Bolca formation is thought to reflect a shallow tropical sea in the western Tethys Ocean with scattered coral reefs. Due to its highly reduced tail, Lessiniabatis likely had a benthic lifestyle, propelling itself with its strengthened pectoral fins.[1] Due to having no known close relatives to compare with, the exact depth range it inhabited is unknown.[5]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Marramà, Giuseppe; Carnevale, Giorgio; Giusberti, Luca; Naylor, Gavin J. P.; Kriwet, Jürgen (2019-10-01). "A bizarre Eocene dasyatoid batomorph (Elasmobranchii, Myliobatiformes) from the Bolca Lagerstätte (Italy) reveals a new, extinct body plan for stingrays". Scientific Reports. 9 (1): 14087. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-50544-y. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 6773687.
- ↑ "Lessiniabatis aenigmatica | Shark-References". shark-references.com. Retrieved 2023-11-25.
- ↑ Lazaro, Enrico de (2019-10-15). "Eocene-Epoch Stingray Had Unique Body Plan | Sci.News". Sci.News: Breaking Science News. Retrieved 2023-11-25.
- ↑ "From the museum, a new race of myliobatiform is found in fossils". Il Bo Live UniPD (in Italian). 2019-10-07. Retrieved 2023-11-25.
- ↑ Marramà, Giuseppe; Carnevale, Giorgio; Kriwet, Jürgen (2021). "Diversity, palaeoecology and palaeoenvironmental significance of the Eocene chondrichthyan assemblages of the Bolca Lagerstätte, Italy". Lethaia. 54 (5): 736–751. doi:10.1111/let.12436. ISSN 0024-1164. PMC 9291491. PMID 35873368.